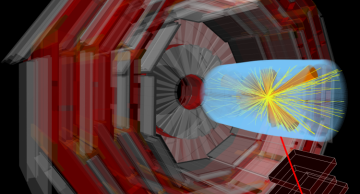
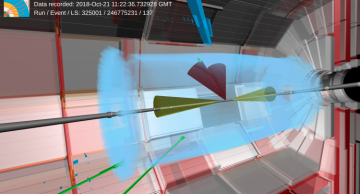
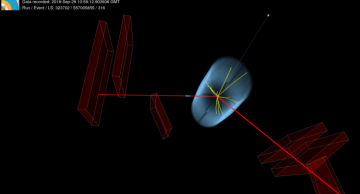
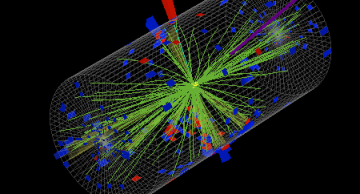
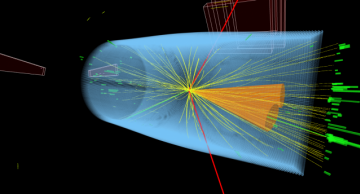
Electromagnetic interactions govern everyday life: You see an object when particles of light deposit energy on the retinas in your eyes. Our sense of touch results from the exchange of the same particles, the photons, between the atoms in our skin…
In the Standard Model of particle physics, at least one Higgs boson is needed to explain fundamental particles’ masses. There is, however, no reason why there needs to be exactly one. On the contrary, many theories of physics beyond the Standard…
The standard model of particle physics encapsulates our current knowledge of elementary particles and their interactions. The standard model is not complete; for example, it does not describe observations such as gravity, has no prediction for dark…
Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD) is the part of the Standard Model of Particle Physics that describes the strong interaction. At relatively low energies, the Constituent Quark Model is a phenomenologically successful effective method to describe…
Fundamental particles are the most basic building blocks of the universe. It took more than 60 years to formulate a physical model to explain their interactions fully. This model is now known as the Standard Model of particle physics. Many of…
Physicists continue to question if the particles we know of are the most fundamental. A new result by the CMS collaboration examines the data collected between 2016 and 2018 for evidence that quarks are composite particles and not elementary. …
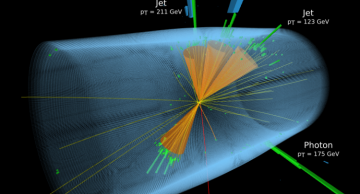
Studying the production of two Higgs bosons is the most obvious way to understand the field responsible for the Higgs boson. A new result by the CMS collaboration gets closer than ever to measuring this field and its physics prediction.
The Higgs…
The Standard Model of Particle Physics is the theory that physicists use to describe elementary particles’ fundamental interactions. The Standard Model was developed over many decades. It has been able to predict experimental observations with…
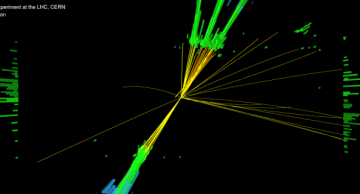
The CMS Collaboration has released a new search for leptoquarks, a hypothetical particle that would be the "missing link" between quarks and leptons. The result has been submitted to the journal Physics Letters B.
All known visible matter that…
What if new particles modify the behaviour of existing particles, but by only a little bit? In a new result, CMS physicists search for new physics using a technique called Effective Field Theory to study the top quark in a "toy universe".…
Eight years ago in 2012, at the largest International Conference on High Energy Physics, the discovery of a new particle carefully coined as Higgs boson-like was announced by the ATLAS and CMS Collaborations. They had seen an excess in data over…
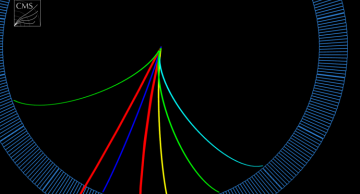
A new result by the CMS collaboration accepted by the journal Physical Review Letters demonstrates for the first time that top quarks are produced in nucleus-nucleus collisions. At the same time, this also demonstrates the capability of the CMS…